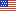
SAE J3400 Charging Connector
In December 2023, SAE International published the Technical Information Report (TIR) for J3400, which is an EV charging connector standard based on the North American Charging Standard (NACS) connector. The standardization of NACS as J3400 ensures that any supplier or manufacturer will be able to use, manufacture, or deploy the J3400 connector on electric vehicles (EVs) and at charging stations across North America.
The NACS connector is one of several connector types that enable fast charging of electric vehicles (EVs), in addition to the Combined Charging System (CCS1) and CHAdeMO. NACS can also be used for AC Level 1 and Level 2 charging and is compatible with the J1772 connector for these charging speeds through an adapter.
In May 2023, the Federal Highway Administration (FHWA) published requirements that allow for J3400/NACS adapters to be installed on all federally funded direct-current fast charging (DCFC) chargers as long as there is also a CCS1 connector.
In August 2024, the SAE EV Coupler Task Force voted to establish the J3400 standard as a Recommended Practice, marking a significant step forward in the standardization process. This milestone brings the J3400 standard closer to official publication in a format that can be cited in regulations and used by manufacturers with confidence.
Background
DCFC enables rapid charging of EVs. There are three types of DCFC connectors in the United States:
CCS1
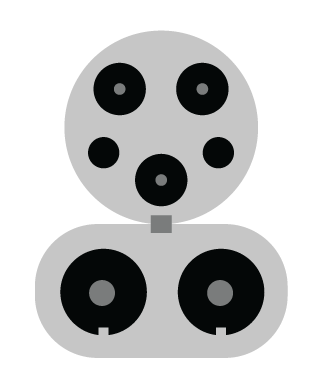
SAE CCS1
CHAdeMO
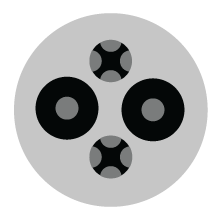
J3400

in development from NACS
Most EV models on the market today charge using the CCS1 connector, but most vehicle manufacturers have made commitments to incorporate the J3400 connector beginning in 2025. These companies have also indicated that they will provide J3400 adapters to owners of CCS vehicles beginning in 2024.
Terminology
When building out EV charging infrastructure, it is helpful to become familiar with industry terminology. The following terms are commonly used:
- Adapter: Hardware that allows an EV to connect to a charger/station that it otherwise could not connect to directly. There are a variety of adapters for different connector types.
- Charger cable: Delivers power from the power source/ charger to the EV.
- Connector: Plugs into a corresponding vehicle charging inlet and makes an electrical connection to charge the EV. Connectors are sometimes also called plugs.
- Charger port or electric vehicle supply equipment (EVSE) port: Each port on a charger can charge a single EV. A port may be able to use multiple connector types (e.g., CHAdeMO, CCS1, NACS). In some cases, multiple connector options may be provided for each port, allowing EVs to use the connector they need, but only one vehicle will charge at a port at a time. The unit that houses ports is sometimes called a charging post, which can have one or more EVSE ports.
- CCS1 connector: Also known as SAE J1772 combo, the Combined Charging System 1 (CCS1) connector uses the same five pin layout for the SAE J1772 connector used for AC Level 1 and Level 2 charging with two additional bottom “DC” pins for use with a DCFC.
- EV charging station location: A site with one or more charging ports at the same address.
- NACS connector: Originally developed by Tesla, this connector works for AC (L1, L2) and DC charging utilizing the same pins for AC and DC power transfer.
- SAE J3400: The SAE standard currently in development for the NACS connector to enable its use across the EV industry.
- Electric Vehicle Charge Controller (EVCC): An embedded controller in the EV responsible for handling communication between an EV and charging station. Standardized communication protocols are key to ensuring compatibility and interoperability between different charging stations and EVs.
- CCS1
- Standardized through SAE J1772
- Developed by industry over a decade of deliberation and field testing.
- J3400
- SAE TIR published in December 2023, Recommended Practice (RP) document expected by September 2024.
- Certification via UL-2251 needs update to both NACS and J3400
- UL Adapter Certification by Q3 2024.
FAQs
23 CFR 680 includes the minimum standards and requirements for projects funded under the National Electric Vehicle Infrastructure (NEVI) Formula Program and projects for the construction of publicly accessible EV chargers that are funded with funds made available under Title 23, United States Code.
23 CFR 680 requires that EV charging stations have at least four network-connected charging ports. Each DCFC charging port must be capable of charging any CCS1-compliant vehicle, and each charging port must have a permanently attached CCS1 connector.
Requiring the CCS1 connector on all federally funded EV charging infrastructure ensures that most vehicles on the road today and those coming to market will be able to charge at federally funded stations. The final rule was modified from its original proposal to allow DCFC charging ports to have other “nonproprietary” connectors so long as each DCFC charging port can charge a CCS1-compliant vehicle.
Takeaway: Federally funded EV chargers can include a J3400 connector if there is also a CCS1 connector that meets the minimum requirements in the final rule.
SAE is an association of engineers and technical experts that among other things, pursues voluntary consensus standards development. The rigorous standardization process ensures technical protocols to enable interoperability, meaning every EV working with every charger. In June 2023, SAE announced the formation of the SAE J3400 NACS Task Force and an expedited process to standardize the NACS connector to become the openly available J3400 connector. The Task Force, which was comprised of over 120 experts from the public and private sectors, developed and subsequently published the J3400 Technical Information Report in December 2023. The TIR will help to ensure that any supplier or manufacturer will be able to use, manufacture, or deploy the J3400 connector on electric vehicles (EVs) and at charging stations across North America.
Additionally, J3400 connectors and cables will need to be certified for safety via the UL 2251 certification standard. UL certification tests are required for electrical devices including charging cables, connectors, and chargers, as a whole or as components, to ensure safe operation. J3400 is a new standard and will need to meet the UL 2251 certification test prior to being placed into service.
Takeaway: The SAE standardization process is a key step in establishing J3400 as an open standard and ensuring it can meet safety, performance, and interoperability criteria.
- November 2022: Tesla renames its previously proprietary connector to NACS and opens the standard to make it available to EV manufacturers in North America.
- June 2023: SAE announces its intent to standardize NACS.
- End of 2023: SAE Hybrid-EV J3400 NACS Electric Vehicle Coupler Task Force publishes a TIR for J3400.
- End of 2023 through early 2024: UL 2252 draft standard for adapters released, and industry consensus period opens.
- January–July 2024: J3400 Connector Design and Release phase begins, and the connector/EVSE System UL 2251 certification testing is performed.
- January–October 2024: Adapter testing and validation phase anticipated to be completed.
- May–October 2024: UL 2252 Certified J3400-CCS adapters anticipated to become available in the market.
- August–October 2024: SAE J3400: NACS Electric Vehicle Coupler J3400 standard to be released.
SAE initiated a task force in June 2023 to expedite the standardization of J3400 by the end of 2023. All major Auto OEM and EV charging companies have announced plans to adopt the J3400 connector as early as 2025. Specific details, including whether CCS1 will be phased out entirely, are still unclear; however, every non-Tesla EV produced through 2024 will continue to have a CCS1 port.
Takeaway: The EV industry has announced plans for widespread adoption of the J3400 connector.
Charging adapters are plugged into the charger unit that match the connector pins used in the EV, enabling EV drivers to use a variety of charging stations regardless of the connector type of the vehicle. A number of automakers have announced they intend to offer adapters so any of their EV models are able to charge with a J3400 connector.
Adapters can be portable or attached as a fixture to a charging station. For example, Tesla has the Magic Dock, an attached NACS-to-CCS1 connector that allows a non-Tesla EV owner to plug in at a Tesla Supercharger station.
For federally funded DCFC, adapters should be a permanently attached connector and have been integrated by the charger manufacturer. The charging station must meet all 23 CFR 680 standards and requirements, including but not limited to interoperability, power level, minimum uptime, and certification by a national recognized testing laboratory as well as to the appropriate UL standards.
Certified CCS1 (vehicle) to J3400 (charger) adapters are anticipated to become available in the market in 2024. Adapters that allow J3400 vehicles to use CCS1 chargers are currently available.
Takeaway: Adapters can be considered eligible under the National Electric Vehicle Infrastructure (NEVI) Formula Program as long as they are permanently attached and meet all 23 CFR 680 standards and requirements.
The National Association of State Energy Officials (NASEO) and the American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials (AASHTO) gathered input via a request for information (RFI) on NACS/J3400 market readiness and standardization.
RFI responses were submitted by Oct. 6., 2023. NASEO received 15 responses, two of which indicated they currently offer a NACS connector. Two responses noted that they expect costs for NACS/J3400 connectors to increase, while most responses did not indicate expected cost for adding NACS/J3400 connectors or retrofitting existing equipment. Six responses indicated that they are waiting for NACS to J3400 standardization before communicating any decisions. Respondents recommended that states maintain flexibility in allowing for the transition to NACS/J3400.
NASEO and AASHTO are also planning to host follow-up conversations with industry and states to facilitate additional information sharing on NACS/J3400 plans and use.
In March 2024, FHWA, in coordination with the Joint Office, released the Request for Information on the J3400 Connector and Potential Options for Performance-Based Charging Standards to solicit input from stakeholders on J3400 market readiness and considerations for potential incorporation into federal requirements. The RFI closed in April 2024. More information is forthcoming.